In this article, we will explore the extent to which government policies address the crucial issue of recycling electric vehicle (EV) batteries. With the rising popularity of EVs, it is essential to address the environmental impact of their battery disposal. By examining the current state of government regulations, we can gain insights into whether adequate measures are being taken to ensure the sustainable management of EV battery waste. Join us on this exploration as we delve into the world of EV battery recycling and its impact on our planet.
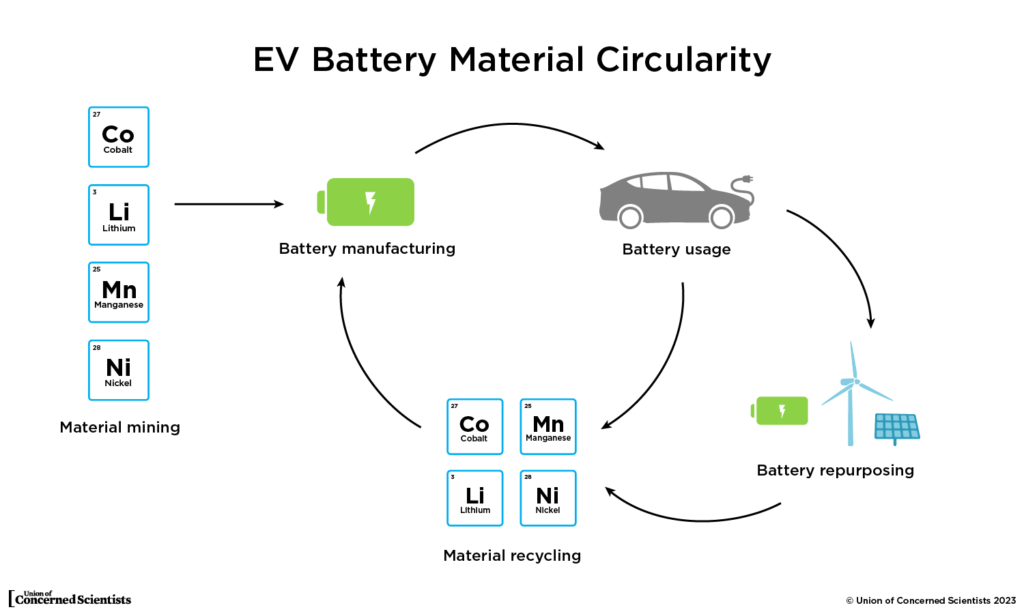
Overview of EV Battery Recycling
Importance of battery recycling
Battery recycling plays a crucial role in the sustainable development of electric vehicles (EVs) as it not only reduces resource depletion but also minimizes the environmental impact associated with battery disposal. EV batteries contain valuable materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which can be recovered and reused through recycling. By recycling batteries, it reduces the need for extracting raw materials, conserves energy, and reduces greenhouse gas emissions.
Challenges in recycling EV batteries
Recycling EV batteries poses several challenges due to their complex composition and the sheer volume of batteries entering the recycling stream. Many of these batteries have varying designs, chemistries, and manufacturing methods, making it difficult to establish a standardized recycling process. Additionally, the collection and transportation of used batteries, as well as the safe handling and disposal of hazardous materials, present logistical challenges. Developing cost-effective recycling technologies and ensuring proper monitoring and compliance are also significant challenges in the industry.
Current Government Policies
National policies on EV battery recycling
Governments around the world are recognizing the importance of regulating and promoting EV battery recycling. Many countries have formulated national policies that outline the responsibilities of battery manufacturers and establish frameworks for the collection, recycling, and disposal of EV batteries. These policies often include targets for battery recycling rates and provide financial incentives to encourage compliance and investment in recycling infrastructure.
International agreements and regulations
In addition to national policies, there is also a growing recognition of the need for international cooperation and standardization in EV battery recycling. International agreements and regulations, such as the Basel Convention on the Control of Transboundary Movements of Hazardous Wastes and their Disposal, aim to regulate the transboundary movement of used batteries and ensure their safe recycling and disposal. These agreements promote information exchange, best practices, and collaboration among countries to tackle the global challenges of battery recycling.
Government Incentives and Initiatives
Financial incentives for battery recycling
To encourage battery recycling, many governments provide financial incentives to stakeholders in the recycling value chain. These incentives may include subsidies, tax credits, or grants to battery manufacturers, recyclers, and collection centers. By offering financial support, governments aim to lower the costs associated with recycling, promote investment in recycling infrastructure, and stimulate the growth of a sustainable and competitive recycling industry.
Research and development projects
Government agencies often invest in research and development projects focused on advancing battery recycling technologies. These projects aim to improve the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of recycling processes, explore new recycling methods, and develop innovative solutions to address the challenges of recycling complex battery chemistries. By supporting research initiatives, governments foster technological advancements and promote the transition towards a circular economy for EV batteries.
Collaboration with the private sector
Government entities collaborate with the private sector to address the challenges and opportunities in EV battery recycling. Partnerships between governments, battery manufacturers, recyclers, and other stakeholders encourage knowledge sharing, information exchange, and technical expertise. By working together, the government and the private sector can drive innovation, develop sustainable recycling practices, and ensure the environmentally sound management of EV batteries throughout their lifecycle.
Role of Government in Collection and Disposal
Establishment of collection centers
Governments play a pivotal role in establishing collection centers where used EV batteries can be safely and conveniently deposited. These centers serve as essential collection points for consumers, ensuring that used batteries are properly handled and do not end up in landfill sites or illegal disposal channels. Governments often collaborate with local governments, retailers, and manufacturers to set up a network of collection centers that facilitate the safe and efficient collection of batteries.
Proper disposal methods for EV batteries
Government policies provide guidelines and regulations for the proper disposal of EV batteries. The disposal of batteries requires careful consideration due to the potentially hazardous materials they contain. Governments work to ensure that used batteries are not disposed of in ways that could harm the environment or human health. They promote the use of authorized recycling facilities or specialized disposal methods that can safely manage the hazardous components of EV batteries, such as heavy metals and toxic chemicals.
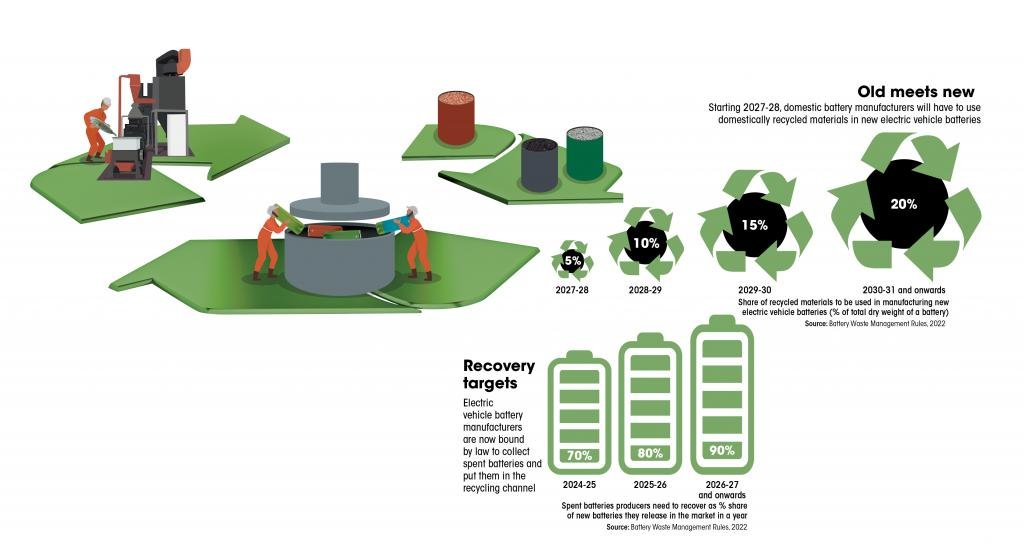
Strategies for Battery Recycling
Development of recycling technologies
Government initiatives focus on supporting the development and improvement of recycling technologies for EV batteries. This includes investments in research and development, offering grants to innovative projects, and fostering partnerships between academia, industry, and government entities. By promoting the development of cutting-edge recycling technologies, governments aim to enhance the efficiency, effectiveness, and environmental performance of the recycling process, ultimately driving the growth of a sustainable battery recycling industry.
Economic viability of recycling processes
Government policies also address the economic viability of battery recycling processes. By providing financial incentives and creating a supportive regulatory framework, governments aim to make battery recycling economically attractive and viable for recycling companies. This includes measures like subsidizing the costs of recycling equipment, establishing market-based incentives for the use of recycled materials, and stimulating demand for recycled batteries through public procurement policies. By addressing the economic aspects, governments aim to create a self-sustainable recycling industry that can thrive in the long run.
Environmental Impacts and Regulations
Ensuring safe recycling practices
Government policies prioritize the enforcement of safe recycling practices to minimize the environmental impact of battery recycling. Regulations set standards for the safe handling, storage, transportation, and treatment of used batteries. Governments establish inspection protocols to ensure that recycling facilities meet these standards and are compliant with environmental regulations. Regular audits and monitoring help ensure that harmful substances are managed responsibly during the recycling process and prevent pollution from occurring.
Monitoring and compliance with environmental regulations
Government agencies are responsible for monitoring and enforcing compliance with environmental regulations related to EV battery recycling. This includes conducting inspections, reviewing documentation, and assessing the environmental performance of recycling facilities. Governments work closely with regulatory bodies and other stakeholders to establish reporting requirements and implement mechanisms for assessing and verifying compliance. By ensuring strict adherence to environmental regulations, governments aim to protect ecosystems, prevent pollution, and promote sustainable recycling practices.

International Cooperation on Battery Recycling
Sharing best practices
Governments actively engage in international cooperation to share best practices in battery recycling. This includes participating in forums, conferences, and working groups where countries can exchange knowledge, expertise, and lessons learned. Governments share information on successful recycling practices, technological advancements, and policy frameworks, allowing countries to learn from one another and adopt strategies proven to be effective. By promoting international collaboration and knowledge-sharing, governments accelerate the development and implementation of sustainable battery recycling practices worldwide.
Global standardization of recycling processes
To facilitate the growth of a global battery recycling industry, governments work towards the standardization of recycling processes and regulations. By developing harmonized guidelines and regulations, governments aim to streamline international trade, ensure the quality and safety of recycled materials, and foster fair competition among recycling companies across borders. Standardization efforts enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of the recycling process, promote resource efficiency, and reduce the environmental footprint of battery recycling on a global scale.
Innovations in Battery Recycling
Exploration of new recycling methods
Governments encourage the exploration and development of new recycling methods for EV batteries. This involves supporting research projects and pilot studies aimed at identifying alternative recycling technologies that can overcome the challenges associated with complex battery chemistries. Innovative methods, such as hydrometallurgical and pyrometallurgical processes, are being explored to recover valuable materials from spent batteries more efficiently. Governments facilitate the testing and demonstration of these new methods, with the goal of promoting breakthroughs and commercializing sustainable recycling technologies.
Advancements in battery design and composition
Government policies also encourage advancements in battery design and composition to facilitate the recycling process. By working closely with battery manufacturers, governments promote the development of batteries that are easier to disassemble and recycle. This includes the use of standardized designs, modular components, and the reduction of hazardous materials in battery chemistries. Governments incentivize manufacturers to adopt eco-design principles and incorporate recyclability criteria into product development, ensuring that future battery generations are more sustainable and compatible with efficient recycling processes.
Future Outlook and Challenges
Scaling up recycling infrastructure
As the adoption of EVs continues to grow, the volume of batteries requiring recycling will increase significantly. To meet this demand, governments must prioritize the scaling up of recycling infrastructure. This involves the expansion of collection centers, the establishment of additional recycling facilities, and the development of robust logistics networks capable of handling the transportation and storage of large quantities of batteries. Governments need to collaborate with industry stakeholders to invest in the necessary infrastructure and ensure the recycling capacity keeps pace with the growing number of EV batteries.
Managing the growing number of EV batteries
The increasing number of EV batteries presents a challenge in terms of managing the volume of batteries reaching their end-of-life. Governments need to establish efficient collection systems and raise awareness among consumers about the importance of returning used batteries for recycling. Additionally, governments can collaborate with manufacturers to promote the implementation of measures such as take-back programs and extended producer responsibility, which hold manufacturers accountable for the collection and recycling of their products.
Addressing potential supply chain issues
The recycling of EV batteries relies on the availability of a secure supply chain for the collection, transportation, and processing of used batteries. Governments must address potential supply chain issues, such as ensuring the proper identification and sorting of used batteries, establishing efficient logistics networks, and fostering collaboration among all stakeholders involved in the recycling value chain. By addressing supply chain challenges, governments can minimize disruptions and promote the smooth flow of batteries through the recycling process.
Conclusion
Government policies play a critical role in addressing the challenges and promoting the sustainable recycling of EV batteries. Through national policies, international agreements, financial incentives, and collaboration with the private sector, governments aim to establish efficient collection systems, develop recycling technologies, and ensure compliance with environmental regulations. By sharing best practices, standardizing recycling processes globally, and fostering innovation, governments are actively working towards a future where the recycling of EV batteries is economically viable, environmentally sound, and capable of meeting the growing demand in a sustainable manner.

