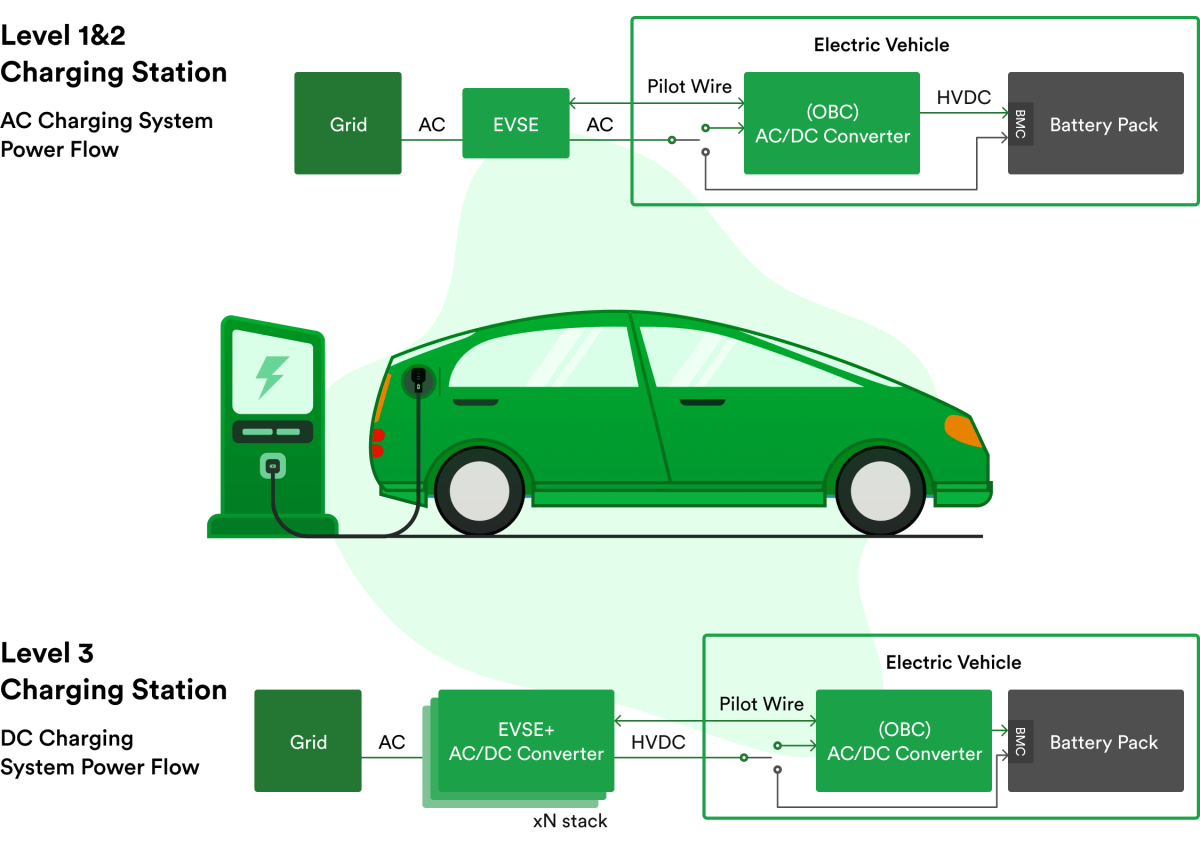
In recent years, the infrastructure for charging electric vehicles has seen significant improvements. With the increasing popularity of electric vehicles, the need for a reliable and accessible charging network has become a top priority. Thanks to advancements in technology and the efforts of various government and private entities, the infrastructure for charging electric vehicles has made remarkable strides. These improvements include the installation of more charging stations in public spaces, the development of fast-charging capabilities, and the implementation of user-friendly mobile apps that help electric vehicle owners easily locate and access charging stations. As a result, the convenience and accessibility of charging electric vehicles have greatly improved, making it more viable than ever before.
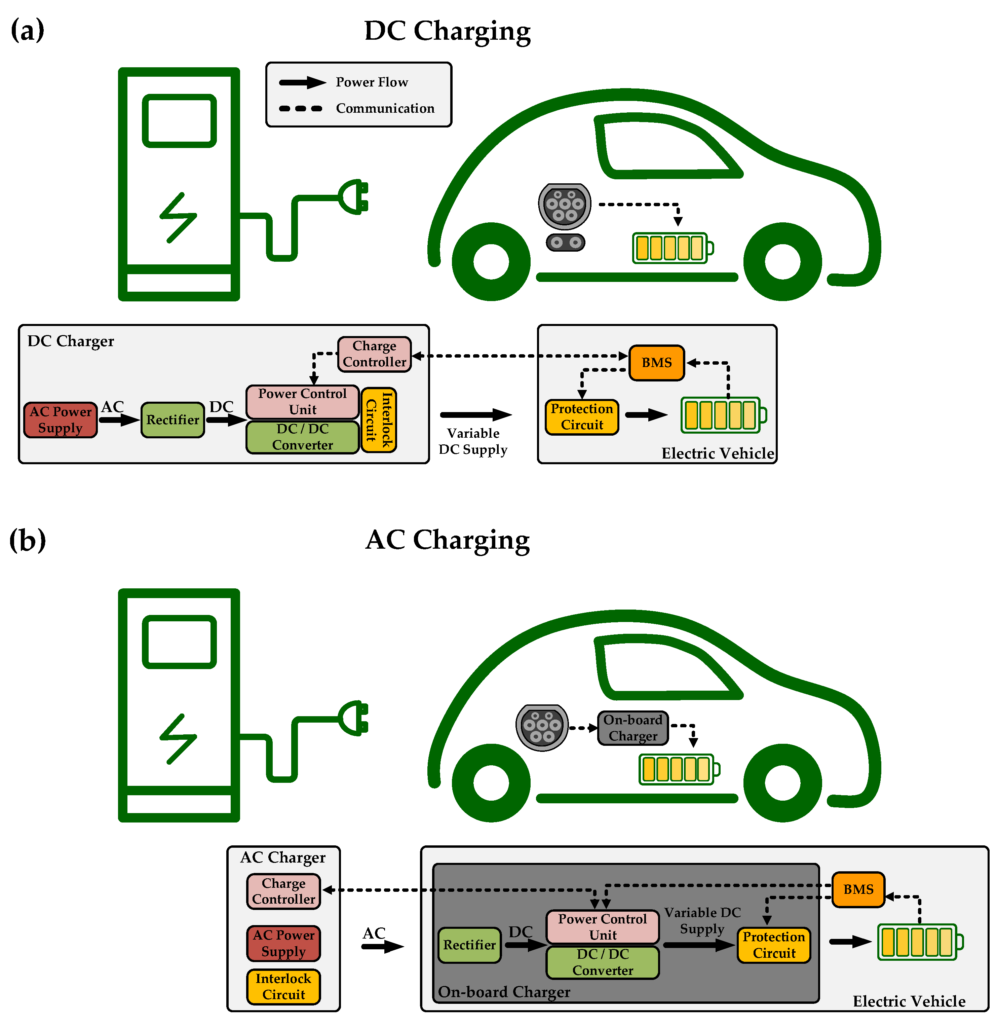
This image is property of www.mdpi.com.
Introduction
Over the past few years, the infrastructure for charging electric vehicles (EVs) has undergone significant improvements and advancements. Increased demand for cleaner and more sustainable transportation options has fueled the expansion of charging stations, leading to a more convenient and accessible charging network for EV owners. Additionally, advancements in charging technology, integration with renewable energy sources, smart grid integration, battery technology enhancements, interoperability and standardization, government support, and private sector investments have all played crucial roles in enhancing the charging infrastructure. In this article, we will explore how these developments have transformed the EV charging landscape and made electric vehicles a more viable and practical option for transportation.
Expansion of Charging Stations
Increase in Public Charging Stations
One of the most significant improvements in EV infrastructure is the substantial increase in public charging stations. In recent years, governments, municipalities, and private businesses have recognized the importance of providing charging infrastructure to support the growing number of electric vehicles on the roads. As a result, there has been a rapid deployment of public charging stations in various locations such as parking lots, shopping malls, workplaces, and even along highways.
The expansion of public charging stations has made it more convenient for EV owners to charge their vehicles while going about their daily activities. With the increase in charging stations, range anxiety, which is a common concern among potential EV buyers, has been alleviated. EV owners now have more options to charge their vehicles, allowing them to confidently plan their trips without worrying about running out of battery power.
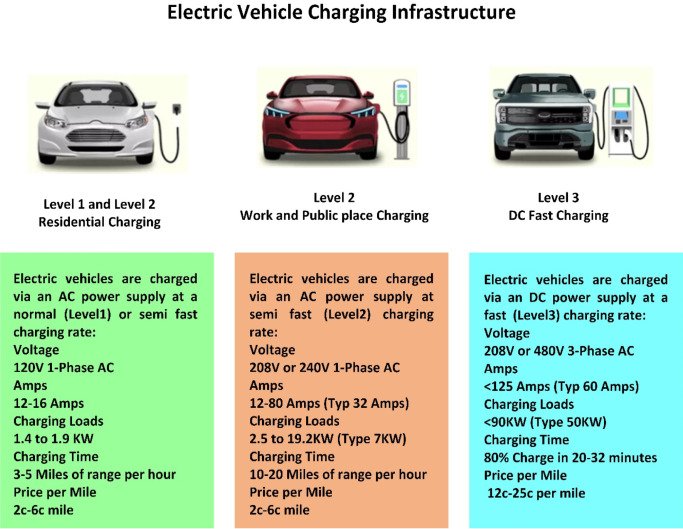
Emergence of Fast Charging Stations
Another significant advancement in the charging infrastructure is the emergence of fast charging stations. Fast charging stations utilize higher voltage and power output to significantly reduce charging times. While regular Level 2 chargers may take several hours to fully charge an EV, fast charging stations can recharge vehicles in a matter of minutes.
The introduction of fast charging stations has improved the overall efficiency and convenience of charging, especially for long-distance travel. EV owners can now take shorter breaks during their journeys to recharge their vehicles, making long road trips more practical and feasible.
Expansion of Home Charging Infrastructure
In addition to the growth of public charging stations, there has been a significant expansion of home charging infrastructure. Many EV owners prefer charging their vehicles at home overnight, as it is convenient and cost-effective. As a result, there has been an increased demand for home charging equipment, such as Level 2 chargers, which can be installed in residential garages or carports.
The expansion of home charging infrastructure has provided EV owners with the flexibility and convenience of charging their vehicles at their own convenience, without the need to visit public charging stations regularly. This allows for a hassle-free charging experience and ensures that the vehicle is always ready for use.
Advancements in Charging Technology
Enhancements in Charging Speed
One of the major advancements in charging technology is the significant improvement in charging speed. Charging speeds have increased significantly over the years, allowing EV owners to charge their vehicles much faster than before. This improvement is largely due to the development of more efficient charging components and advanced power electronics.
Faster charging speeds enable EV owners to quickly recharge their vehicles during short stops, such as during a lunch break or while running errands. This makes owning an EV more convenient, as it reduces the waiting time associated with charging and allows for more flexibility in daily routines.
Improved Charging Efficiency
Alongside faster charging speeds, charging efficiency has also improved in recent years. Charging efficiency refers to the amount of energy that is transferred from the charging station to the vehicle’s battery during the charging process. Higher charging efficiency means less energy is lost as heat during charging, resulting in a more sustainable and efficient charging infrastructure.
Improved charging efficiency reduces energy waste and minimizes costs for EV owners and charging station operators. Additionally, it contributes to the overall sustainability of EV adoption by enabling more effective use of electric grid resources.
Development of Wireless Charging
Wireless charging has emerged as a promising technology in the field of EV charging. It allows for the charging of vehicles without the need for physical cables and connectors. Instead, charging occurs through an electromagnetic field created between a charging pad on the ground and a receiver installed on the vehicle.
The development of wireless charging technology addresses the convenience and ease-of-use concerns associated with traditional plug-in charging methods. It eliminates the need for manual connections between the charging equipment and the vehicle, simplifying the charging process for EV owners.
Introduction of Vehicle-to-Grid Technology
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology is an innovative concept that allows electric vehicles to not only draw power from the grid but also push power back into it. With V2G technology, EVs can act as energy storage devices, contributing to grid stability and managing energy demand fluctuations.
The introduction of V2G technology opens up new possibilities for the integration of EVs into the energy grid. It enables EV owners to participate in demand response programs, where they can sell surplus energy stored in their vehicle’s battery back to the grid during peak demand periods. This not only benefits the grid by alleviating stress during high demand periods but also provides financial incentives for EV owners.
Integration with Renewable Energy
Growing Implementation of Solar-Powered Charging Stations
The integration of EV charging infrastructure with renewable energy sources has gained significant momentum in recent years. Solar-powered charging stations have become increasingly popular as they provide a sustainable and clean source of energy for charging electric vehicles.
Solar-powered charging stations utilize photovoltaic panels to convert sunlight into electricity, which is then used to charge EVs. By utilizing solar energy, these charging stations reduce reliance on the grid for electricity, minimize the carbon footprint of EV charging, and promote the use of renewable energy sources.
Utilization of Wind Energy for Charging Infrastructure
Similar to solar power, wind energy is also being used to power EV charging infrastructure. Wind turbines generate electricity from the motion of the wind, which can be harnessed to charge electric vehicles.
This integration of wind energy with charging infrastructure adds another renewable energy source to the mix, further enhancing the sustainability of EV charging. It allows EV owners to charge their vehicles while minimizing their impact on the environment and reducing dependence on non-renewable sources of electricity.
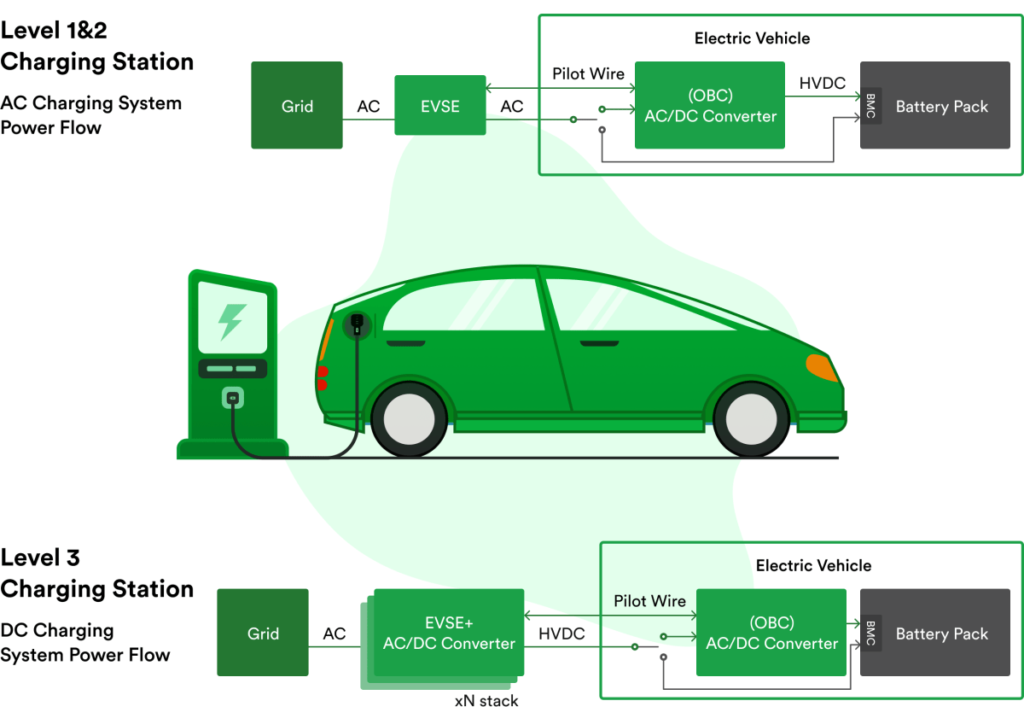
This image is property of www.rinf.tech.
Smart Grid and Demand Response
Integration of Electric Vehicle Charging with Smart Grid
The integration of electric vehicle charging with the smart grid is a key development in the advancement of EV charging infrastructure. The smart grid is an intelligent electricity distribution network that utilizes advanced communication and control technologies to optimize energy generation, distribution, and consumption.
By integrating EV charging with the smart grid, charging patterns can be dynamically managed to ensure optimal use of resources. For example, EVs can be charged during off-peak hours when electricity demand is lower, reducing the strain on the grid during peak periods. This not only benefits the overall grid stability but also allows EV owners to take advantage of lower electricity rates during off-peak hours.
Demand Response Programs for Load Management
Demand response programs have emerged as effective tools for load management, especially in the context of EV charging infrastructure. These programs incentivize EV owners to change their charging patterns based on grid conditions and demand fluctuations.
Through demand response programs, EV owners can receive financial incentives or other rewards for charging their vehicles during periods of low demand or when renewable energy generation is high. This incentivizes EV owners to align their charging behavior with the needs of the grid, ultimately enhancing the overall efficiency and sustainability of the charging infrastructure.
Battery Technology and Range Anxiety
Advancements in Lithium-ion Battery Development
The development of lithium-ion batteries has revolutionized the electric vehicle industry and significantly improved the charging infrastructure. Lithium-ion batteries offer high energy density, longer lifespan, and faster charging capabilities compared to conventional battery technologies.
Advancements in lithium-ion battery technology have resulted in higher energy storage capacities, allowing EVs to travel longer distances on a single charge. This, in turn, reduces range anxiety, which refers to the fear of running out of battery power before reaching a charging station.
Progress in Battery Energy Density
Battery energy density, which refers to the amount of energy that can be stored in a given volume or weight of the battery, has also seen significant progress in recent years. Higher battery energy density translates to increased range per charge, enabling EV owners to travel longer distances without the need for frequent charging.
Improvements in battery energy density have contributed to the increased adoption of EVs by addressing one of the key concerns of potential buyers – range limitations. With each new generation of batteries, EVs are becoming more capable of covering larger distances, making them a more practical option for daily commuting and long-distance travel.
Mitigating Range Anxiety through Extended Range and Fast Charging
The combination of advancements in battery technology, increased charging speed, and the expansion of charging infrastructure has effectively mitigated range anxiety. EV owners now have access to fast charging stations that can rapidly recharge their vehicles and extend their driving range.
With the availability of fast charging infrastructure and improved battery energy density, EV owners can confidently plan their journeys without worrying about running out of battery power. This has significantly reduced range anxiety and increased the overall confidence and acceptance of EVs among consumers.
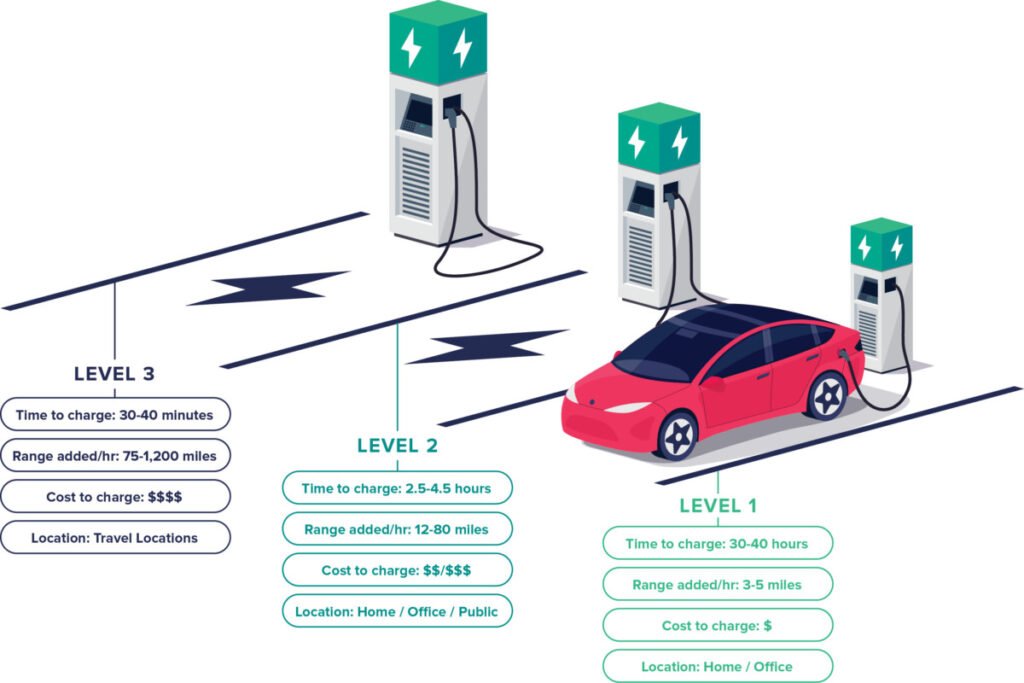
This image is property of www.ssr-inc.com.
Interoperability and Standardization
Development of Universal Charging Standards
Interoperability and standardization are crucial for the widespread adoption and success of the EV charging infrastructure. The development of universal charging standards, such as the Combined Charging System (CCS) and CHAdeMO, has played a significant role in promoting interoperability among different charging networks and ensuring compatibility between charging equipment and EVs.
Universal charging standards enable EV owners to access charging stations regardless of the charging network operator or charging infrastructure provider. This eliminates the need for multiple charging adapters and simplifies the charging process for EV owners, making it more user-friendly and convenient.
Efforts for Interoperability among Charging Networks
In addition to universal charging standards, there have been ongoing efforts to promote interoperability among different charging networks. Various industry collaborations and initiatives aim to establish seamless roaming capabilities between charging networks, allowing EV owners to access charging stations from different providers using a single payment and authentication system.
Efforts for interoperability contribute to the convenience and ease of use of the EV charging infrastructure. They ensure that EV owners can charge their vehicles wherever they go, regardless of the network operator or charging provider, further enhancing the accessibility and usability of EVs.
Incentives and Government Support
Financial Incentives for Charging Infrastructure Deployment
To encourage the expansion of the EV charging infrastructure, many governments and organizations offer financial incentives for the deployment of charging stations. These incentives often come in the form of grants, subsidies, or tax credits to incentivize businesses and individuals to invest in charging infrastructure.
Financial incentives play a crucial role in accelerating the growth of the charging infrastructure by reducing the upfront costs and investment risks associated with building and operating charging stations. They encourage private businesses and charging infrastructure providers to invest in the necessary infrastructure, thereby ensuring the availability and accessibility of charging stations for EV owners.
Government Funding and Grants for Charging Stations
In addition to financial incentives for infrastructure deployment, governments also provide direct funding and grants for the construction and operation of charging stations. This funding helps cover the costs associated with installing charging equipment, establishing charging networks, and maintaining the infrastructure.
Government funding and grants are essential for expanding the charging infrastructure, particularly in areas where the private sector investment may be limited. By providing financial support, governments ensure the widespread availability of charging stations, making EV adoption more practical and viable for consumers.

This image is property of www.airswift.com.
Private Sector Investment
Increased Investments from Automakers and Energy Companies
The private sector, particularly automakers and energy companies, has been actively investing in the expansion of the EV charging infrastructure. Automakers recognize the need for a reliable and convenient charging network to support their electric vehicle offerings, and they have been partnering with charging infrastructure providers or establishing their own charging networks.
Similarly, energy companies have identified the growing demand for electric vehicles and the associated need for charging infrastructure. They have made significant investments in creating charging networks and integrating EV charging with their energy distribution systems. These investments help ensure the availability of charging infrastructure and contribute to the overall growth of the EV market.
Expansion of Charging Networks by Private Players
Private companies and startups specializing in EV charging have also played a significant role in expanding the charging infrastructure. These players have focused on establishing charging networks in strategic locations such as shopping malls, highway rest areas, and urban centers.
The expansion of charging networks by private players has increased the accessibility of charging stations, ensuring that EV owners have a wide range of options for charging their vehicles. It has also spurred competition in the charging market, leading to innovation and the continuous improvement of charging services.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the infrastructure for charging electric vehicles has significantly improved in recent years, driven by advancements in technology, integration with renewable energy, smart grid integration, battery technology enhancements, interoperability and standardization efforts, government support, and private sector investments. The expansion of charging stations, the emergence of fast charging stations, the development of wireless charging, and the introduction of vehicle-to-grid technology have all contributed to enhancing the charging infrastructure and making EVs a more practical and convenient transportation option. With continued advancements and investments in EV charging infrastructure, electric vehicles are set to become even more accessible and sustainable in the years to come.
This image is property of ars.els-cdn.com.